Overview of Spaghetti Models and Beryl
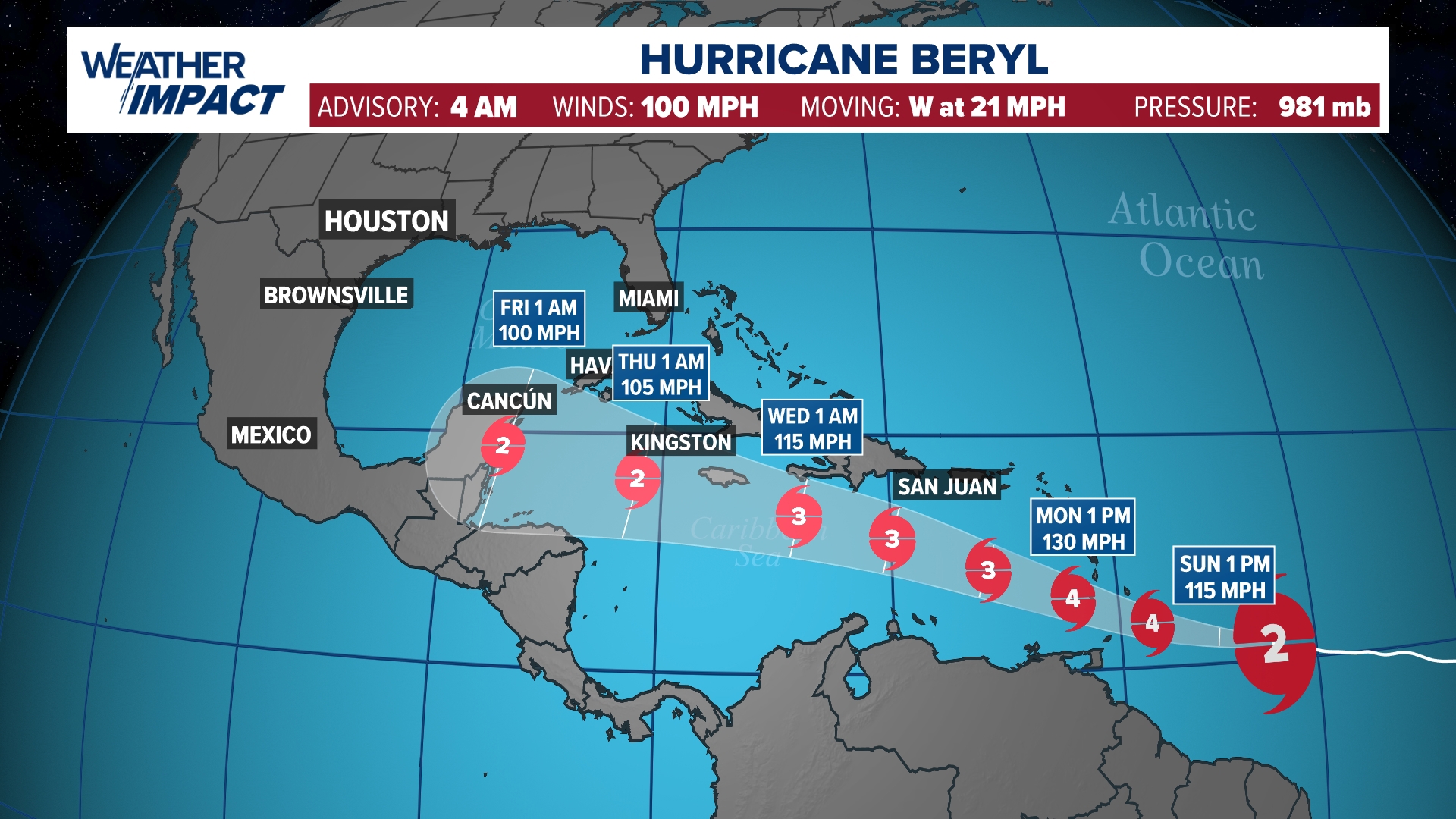
Spaghetti models beryl – Spaghetti models, also known as ensemble models, are a type of numerical weather prediction (NWP) model that involves running multiple simulations of the same weather forecast with slightly different initial conditions. The goal of spaghetti models is to provide a range of possible weather outcomes, rather than a single deterministic forecast. This range of outcomes is represented by a collection of lines on a map, which resemble a bundle of spaghetti noodles. The spread of these lines indicates the level of uncertainty in the forecast.
Spaghetti models beryl are weather forecasting tools that predict the potential path of a hurricane. These models use a variety of data, including historical hurricane data, to create a range of possible tracks for the storm. For hurricane beryl spaghetti models, you can check out hurricane beryl spaghetti models to see the forecasted tracks.
Spaghetti models beryl can be helpful for emergency planners and residents in the path of a hurricane to make informed decisions about evacuation and preparedness.
The Beryl satellite mission is an Earth observation satellite launched by the European Space Agency (ESA) in 2018. Beryl is equipped with a radar altimeter that measures the height of the sea surface. This data can be used to derive information about ocean currents, which are important for understanding global climate patterns and predicting weather events.
Spaghetti models Beryl are popular due to their flexibility. These models have a variety of uses, including forecasting weather patterns and predicting the spread of diseases. You can learn more about spaghetti models by clicking on the link. Spaghetti models Beryl are particularly useful for predicting the path of hurricanes.
The integration of spaghetti models and Beryl data has the potential to improve the accuracy of ocean current analysis. By combining the range of possible weather outcomes from spaghetti models with the precise measurements of sea surface height from Beryl, scientists can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the dynamics of ocean currents.
Integration of Spaghetti Models and Beryl Data
The integration of spaghetti models and Beryl data is a complex process that involves several steps. First, the spaghetti model outputs are processed to extract information about the wind and pressure fields. This information is then used to drive an ocean model, which simulates the movement of ocean currents. The Beryl data is used to calibrate and validate the ocean model, ensuring that it produces accurate simulations of the real world.
The integrated spaghetti model-Beryl system has been used to study a variety of oceanographic phenomena, including the Gulf Stream and the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). The system has also been used to develop early warning systems for coastal hazards, such as storm surges and tsunamis.
Applications and Examples of Spaghetti Models with Beryl Data
Spaghetti models are valuable tools for analyzing and visualizing ocean currents. They provide insights into the dynamics of ocean circulation and support various research and operational applications.
One notable application of spaghetti models with Beryl data is studying ocean currents in the North Atlantic. Researchers have used these models to examine the variability of the Gulf Stream, a major current that transports warm water from the tropics to the North Atlantic. Spaghetti models help identify areas of high and low current variability and track the movement of water masses over time.
In the Pacific Ocean, spaghetti models have been employed to study the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), a climate phenomenon that affects global weather patterns. These models have provided valuable insights into the evolution and propagation of ENSO events and their impact on ocean circulation and marine ecosystems.
Analyzing Beryl data with spaghetti models involves several steps. First, the data is preprocessed to remove noise and correct for errors. Then, the data is interpolated onto a regular grid to create a continuous representation of the ocean currents. Finally, the spaghetti models are applied to generate ensembles of possible current trajectories.
By analyzing the spaghetti models, researchers can identify regions of strong and weak currents, determine the direction and speed of water movement, and study the temporal evolution of ocean circulation patterns.
Case Studies
One specific case study where spaghetti models have enhanced our understanding of ocean circulation is the study of the Agulhas Current in the Indian Ocean. This current plays a crucial role in transporting heat and salt between the Indian and Atlantic Oceans. Spaghetti models have helped researchers track the path of the Agulhas Current and identify the factors that influence its variability.
Another case study is the use of spaghetti models to investigate the circulation patterns in the Arctic Ocean. These models have provided insights into the movement of sea ice and the transport of freshwater and nutrients in the Arctic region.
Spaghetti models have also been used to study the impact of climate change on ocean circulation. By simulating future climate scenarios, researchers can assess how ocean currents may change and how these changes could affect marine ecosystems and coastal communities.
Overall, spaghetti models are powerful tools for studying ocean currents and gaining a better understanding of ocean circulation patterns. They have been used in a wide range of applications, from basic research to operational forecasting, and have contributed significantly to our knowledge of the ocean.
Advanced Techniques and Future Directions: Spaghetti Models Beryl
Beryl data integration in spaghetti models has opened up new avenues for advanced techniques and future research directions.
Data Assimilation and Ensemble Forecasting
Data assimilation is a technique used to incorporate Beryl data into numerical weather prediction (NWP) models. This process involves merging Beryl data with model forecasts to produce a more accurate initial condition for the model. Ensemble forecasting is a technique that involves running multiple model forecasts with slightly different initial conditions. By combining the results of these forecasts, ensemble forecasting can provide a more robust prediction of the weather.
Applications for Extreme Event Prediction and Weather Forecasting, Spaghetti models beryl
Spaghetti models with Beryl data have the potential to improve the prediction of extreme events, such as hurricanes and floods. By providing a more accurate representation of the uncertainty in the forecast, spaghetti models can help decision-makers prepare for and mitigate the impacts of these events. Spaghetti models can also be used to improve the accuracy of weather forecasts, particularly in regions where Beryl data is available.
Future Research and Development
There are several areas for future research and development in the field of spaghetti models and Beryl data integration. These include:
- Developing more advanced data assimilation techniques to better incorporate Beryl data into NWP models.
- Improving the accuracy of ensemble forecasting by using more sophisticated techniques.
- Exploring new applications of spaghetti models with Beryl data, such as for climate prediction and seasonal forecasting.